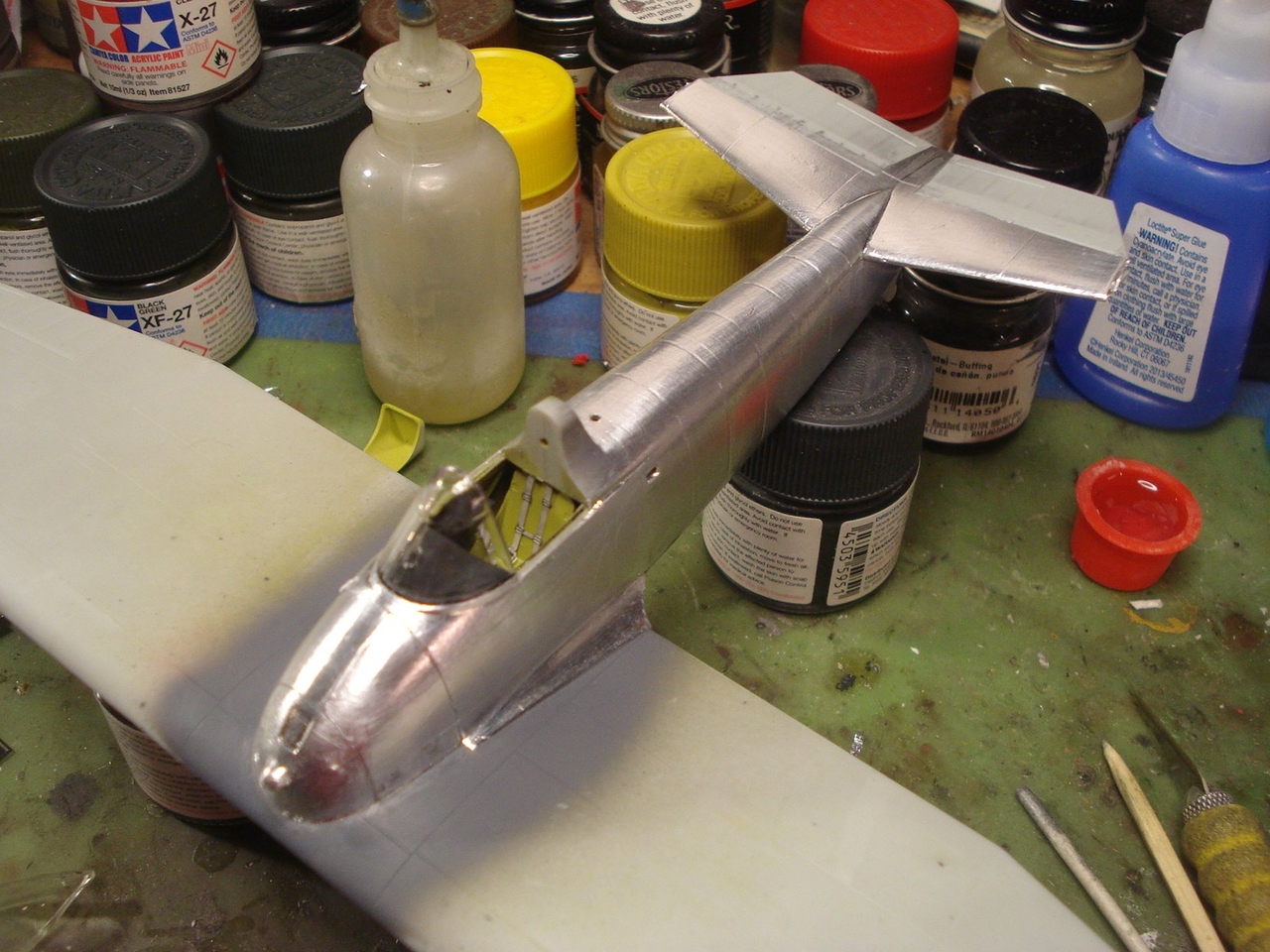
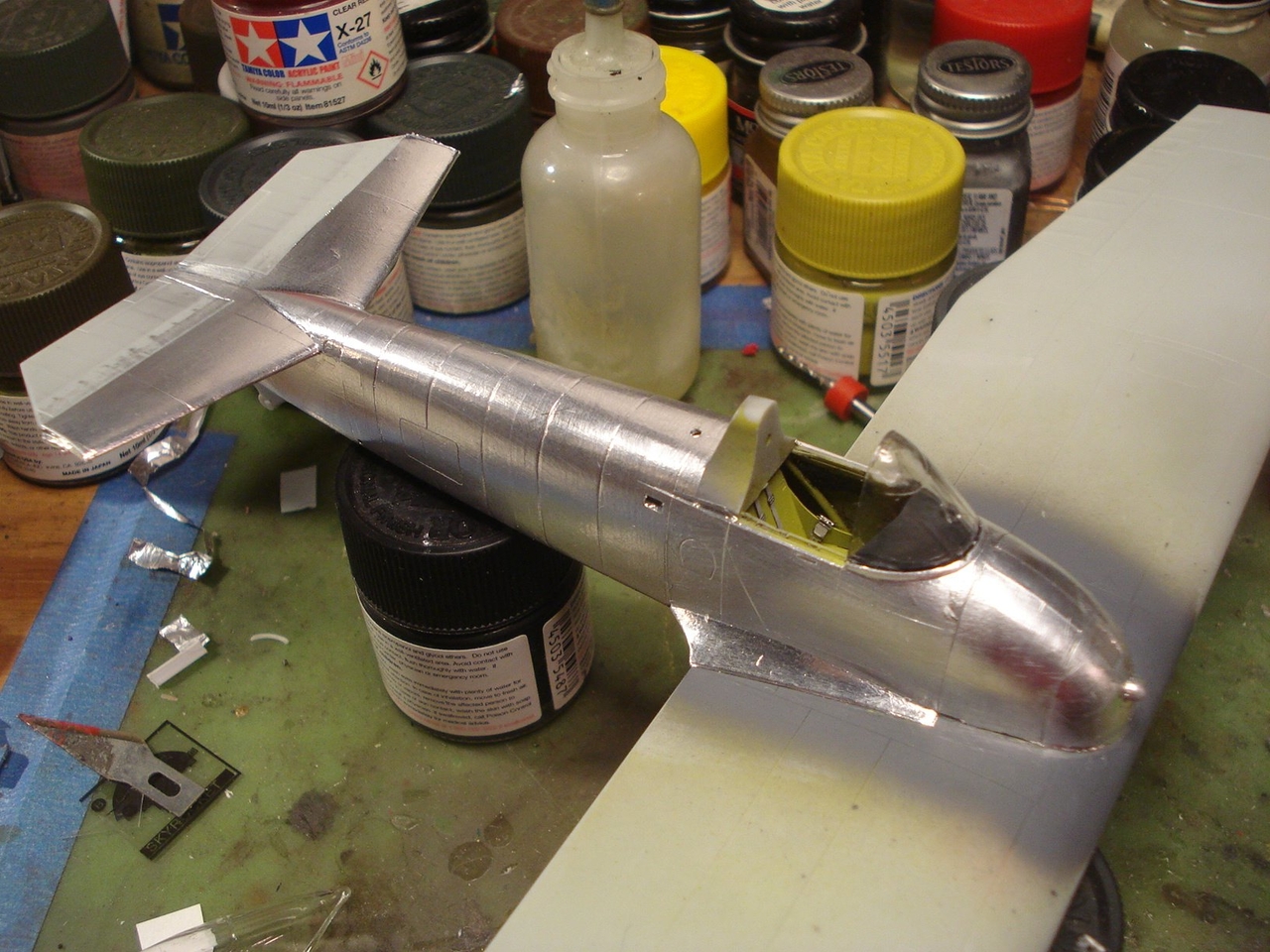
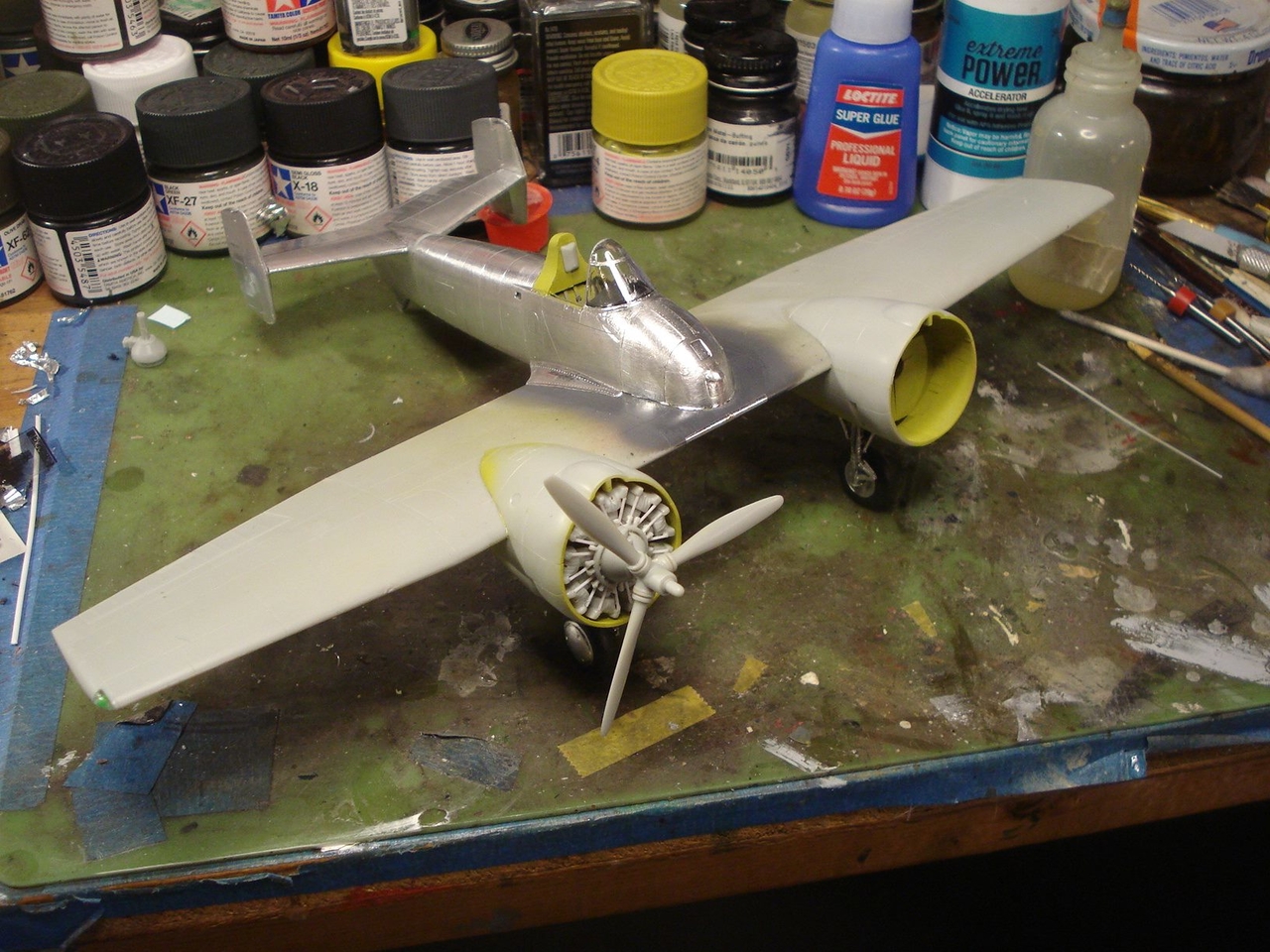
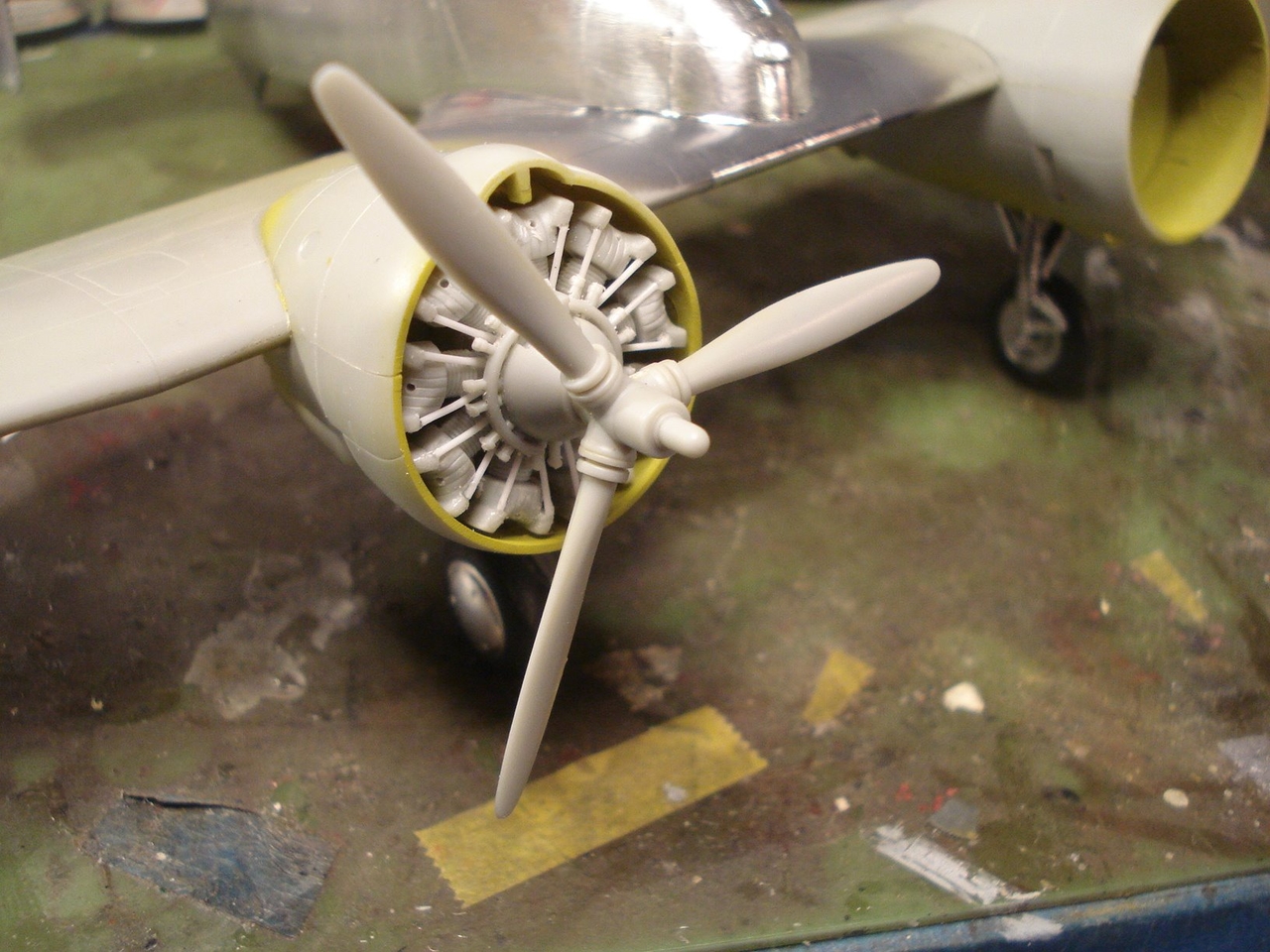
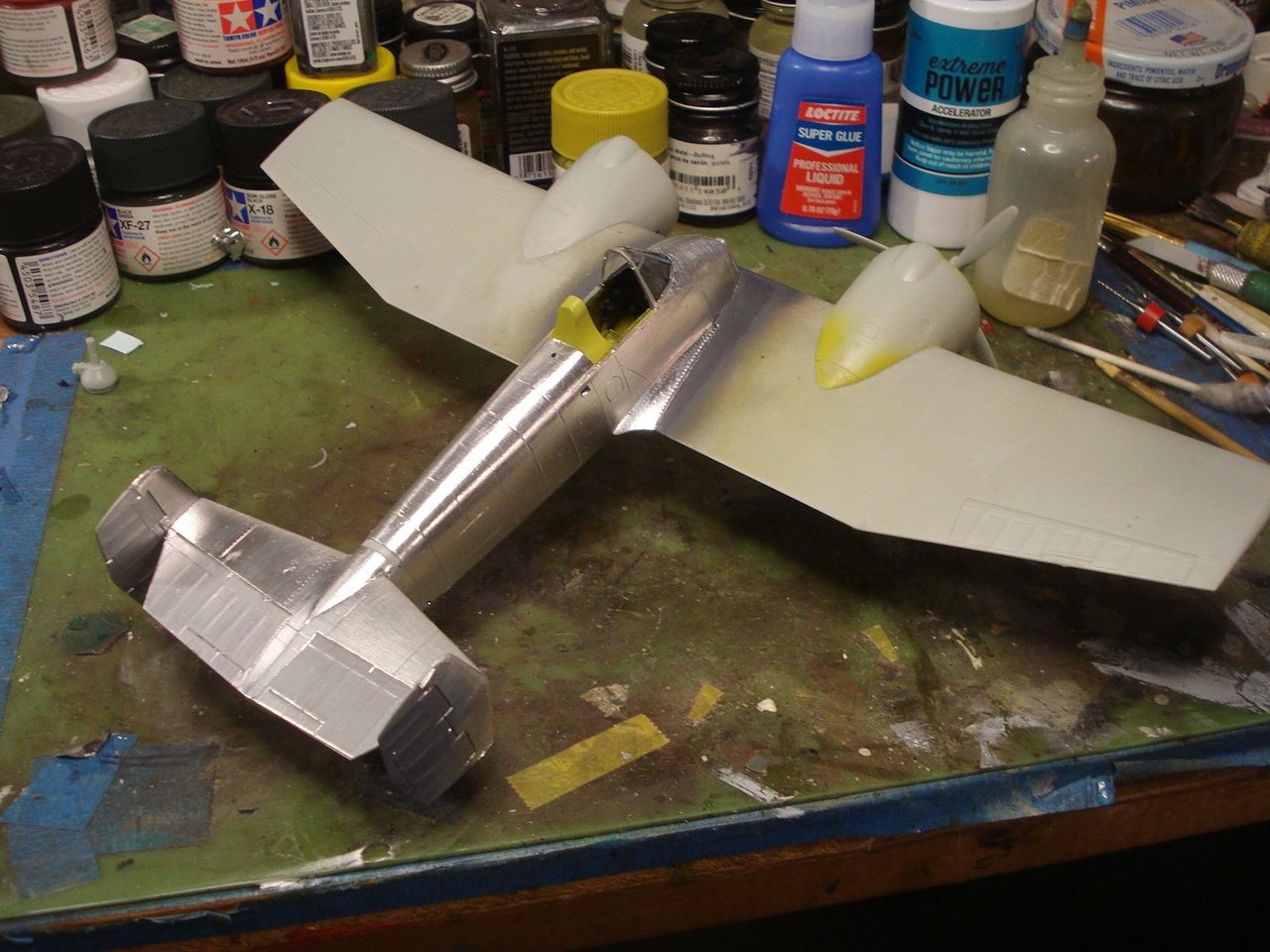
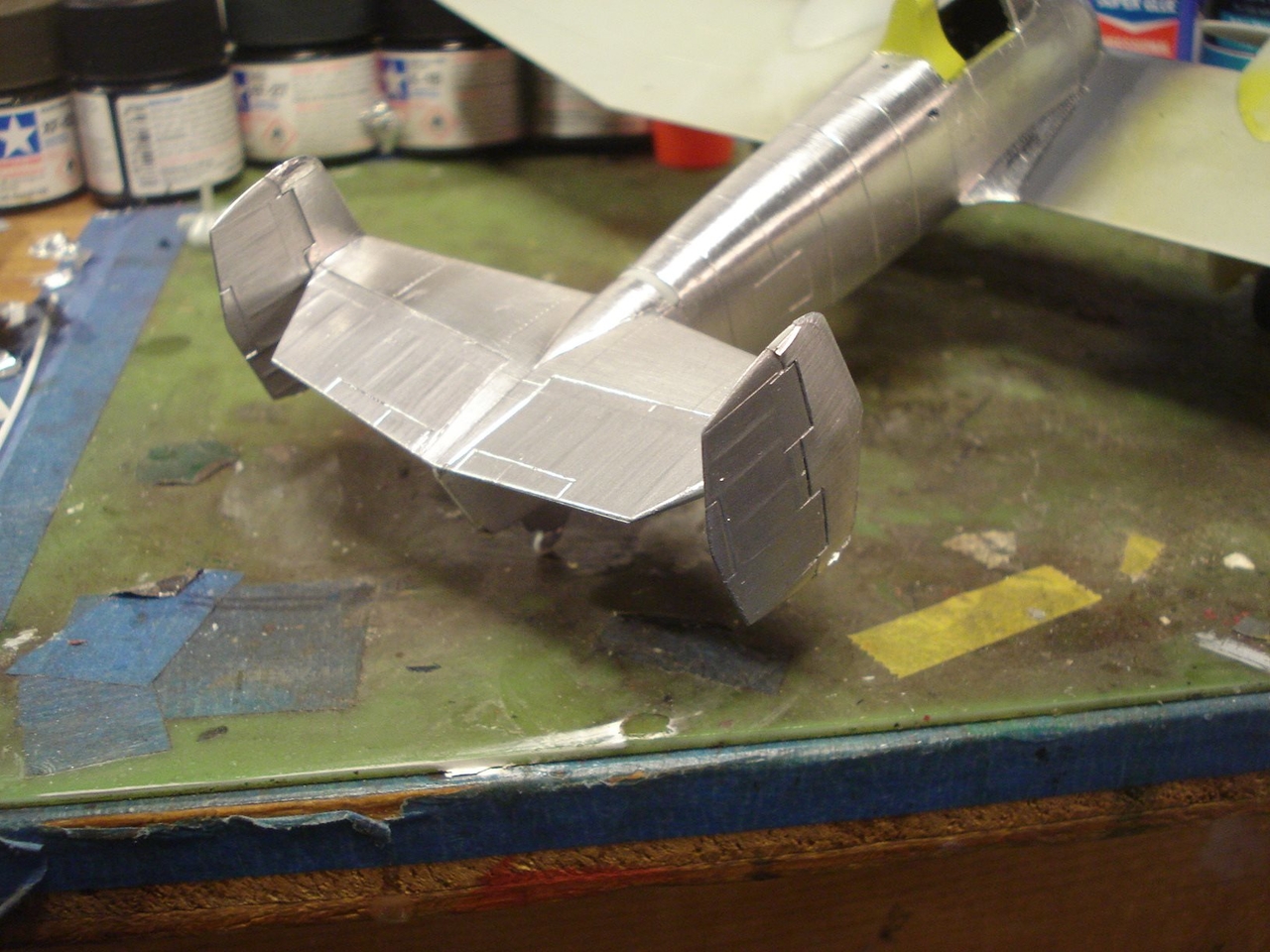
I will attempt the XF5F-1 Grumman Skyrocket flown by B.A. Gilles.


The Grumman XF5F Skyrocket was a prototype twin-engined shipboard fighter interceptor. The U. S. Navy ordered one prototype, model number G-34, from Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation on 30 June 1938; its designation was XF5F-1. The aircraft had a unique appearance: The forward "nose" of the fuselage did not extend forward of the wing. Provisions were included for two 23 mm (0.906 in) Madsen cannon as armament.
In 1938 Grumman presented a proposal to the U. S. Navy for a twin engine carrier based aircraft, unlike any other fighter aircraft that had ever been considered. The design was for a light weight fighter (under 10,000 lbs maximum takeoff weight) powered by two 1,200 hp Wright R-1820 engines, with propellers geared to rotate in opposite directions to cancel out the effects of each engine's torque, promising high-speed, and an outstanding rate of climb.
The XF5F Skyrocket was a low wing monoplane with a short fuselage that began aft of the wing's leading edge with a twin tail assembly that featured a pronounced dihedral to the horizontal stabilizer. The main landing gear and tail wheel were fully retractable.
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 28 ft 9 in (8.76 m)
Wingspan: 42 ft (12.80 m)
Height: 11 ft 4 in (3.45 m)
Wing area: 303.5 ft2 (28.2 m2)
Empty weight: 8,107 lb (3,600 kg)
Loaded weight: 10,138 lb (4,600 kg)
Max. takeoff weight: 10,900 lb (5450 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Wright XR-1820-40/42 Cyclone nine cylinder radial air-cooled engine, 1,200 hp (895 kW) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 383 mph at sea level (616 km/h)
Range: 1,200 mi (1,800 km)
Service ceiling: 33,000 ft (11,000 m)
Rate of climb: 4,000 ft/min (1,220 m/min)
Armament
4 × 0.5 in (12.7 mm) machine guns
2 × 165 lb (75 kg) bombs
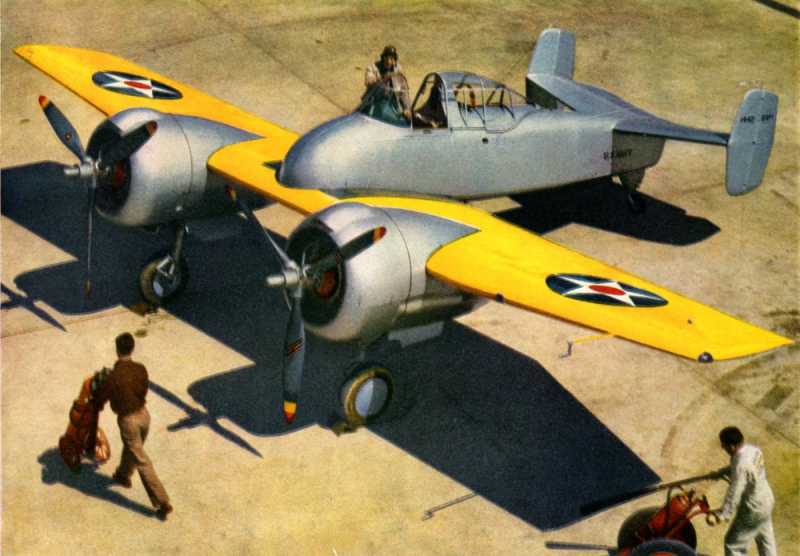







The Grumman XF5F Skyrocket was a prototype twin-engined shipboard fighter interceptor. The U. S. Navy ordered one prototype, model number G-34, from Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation on 30 June 1938; its designation was XF5F-1. The aircraft had a unique appearance: The forward "nose" of the fuselage did not extend forward of the wing. Provisions were included for two 23 mm (0.906 in) Madsen cannon as armament.
In 1938 Grumman presented a proposal to the U. S. Navy for a twin engine carrier based aircraft, unlike any other fighter aircraft that had ever been considered. The design was for a light weight fighter (under 10,000 lbs maximum takeoff weight) powered by two 1,200 hp Wright R-1820 engines, with propellers geared to rotate in opposite directions to cancel out the effects of each engine's torque, promising high-speed, and an outstanding rate of climb.
The XF5F Skyrocket was a low wing monoplane with a short fuselage that began aft of the wing's leading edge with a twin tail assembly that featured a pronounced dihedral to the horizontal stabilizer. The main landing gear and tail wheel were fully retractable.
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 28 ft 9 in (8.76 m)
Wingspan: 42 ft (12.80 m)
Height: 11 ft 4 in (3.45 m)
Wing area: 303.5 ft2 (28.2 m2)
Empty weight: 8,107 lb (3,600 kg)
Loaded weight: 10,138 lb (4,600 kg)
Max. takeoff weight: 10,900 lb (5450 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Wright XR-1820-40/42 Cyclone nine cylinder radial air-cooled engine, 1,200 hp (895 kW) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 383 mph at sea level (616 km/h)
Range: 1,200 mi (1,800 km)
Service ceiling: 33,000 ft (11,000 m)
Rate of climb: 4,000 ft/min (1,220 m/min)
Armament
4 × 0.5 in (12.7 mm) machine guns
2 × 165 lb (75 kg) bombs